Ictalurus dugesii
Lerma Catfish
Larry PageIdentification
The Lerma Catfish has 11-13 short rakers on the 1st gill arch, and usually 9-10 pectoral fin rays and 20-27 anal rays. The length of the dorsal spine is shorter or equal to the fleshy interorbital distance. There are 5-14 large serrae on pectoral spine of juvenile. The supraoccipital spine is not in contact with the supraneural.
Range
The Lerma Catfish occurs in the Rio Lerma and Rio Ameca drainages on the Pacific Slope of Mexico.

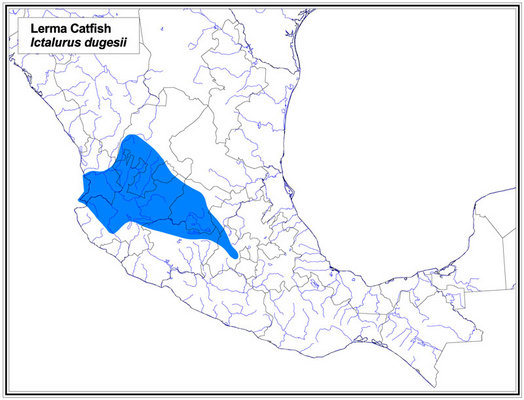
Distribution of Ictalurus dugesii © Larry Page
Habitat
The Lerma Catfish lives in clear to turbid, quiet pools over rock, sand or mud in creeks and small to medium-sized rivers and reservoirs. Often found near vegetation.
Similar Species
The Headwater Catfish, I. lupus, has 13-17 long rakers on the 1st gill arch. The Yaqui Catfish, I. pricei, has 16-24 rakers on the 1st gill arch and usually 11 pectoral fin rays. The Rio Verde Catfish, I. mexicanus, has the dorsal spine longer than the fleshy interorbital distance and 2-3 very small serrae on the pectoral spine of the juvenile. The Channel Catfish, I. punctatus, has 26-32 anal rays and the supraoccipital spine in contact with the supraneural.
About This Page
Larry Page

Florida Museum of Natural History, Gainesville, Florida, USA
Correspondence regarding this page should be directed to Larry Page at and Griffin Sheehy at
Page copyright © 2007 Larry Page
All Rights Reserved.
- First online 23 May 2007
- Content changed 23 May 2007
Citing this page:
Page, Larry. 2007. Ictalurus dugesii . Lerma Catfish. Version 23 May 2007 (under construction). http://tolweb.org/Ictalurus_dugesii/69932/2007.05.23 in The Tree of Life Web Project, http://tolweb.org/





 Go to quick links
Go to quick search
Go to navigation for this section of the ToL site
Go to detailed links for the ToL site
Go to quick links
Go to quick search
Go to navigation for this section of the ToL site
Go to detailed links for the ToL site