Stoloteuthis sp. A
Richard E. YoungIntroduction
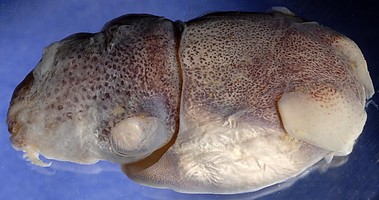
Figure.This was the title photograph when Stoloteuthis sp. A
was originally described as Heteroteuthis sp. A.
When this species was first described on the Tree of Life, it was known from only a single female which had the basic shape of a species of Heteroteuthis especially with its anteriorly located ventral shield and, therefore, was descibed as an unrecognized species, Heteroteuthis sp. A. Now with several more specimens including mature males, the species clearly does not belong in Heteroteuthis. Its placement, however, is uncertain as it shows strong similarities to both Stoloteuthis and Sepiolina but is placed in the latter for reasons stated under "Phylogenetic relationships" below.
Brief diagnosis:
A Stoloteuthis with ...
- deep, angled posterior pit in funnel-locking groove.
- fused nuchal cartilage but free dorsal mantle margin.
- ventral shield restricted to anterior third of mantle.
The second feature is unique.
Characteristics
- Arms (female)
- Arm formula: 3>1=2=4.
- Tips (distal 10% of arm) without suckers on arms I, III and IV; arms II with suckers to tip.
- Arms I and III with keels especially broad distally. Arms II virtually without keels, arms IV with lateral membrane.
- Suckers of dorsal and ventral series on arms identical to one another.
- Web ...
- Arm formula: 3>1=2=4.
- Arms (male).
- Arm formula: III>I=II>IV. Arms I and IV rather blunt; arms II and III attenuate; arms I very broad broad (hectocotylized); all arms without broad distal keels.
 Click on an image to view larger version & data in a new window
Click on an image to view larger version & data in a new window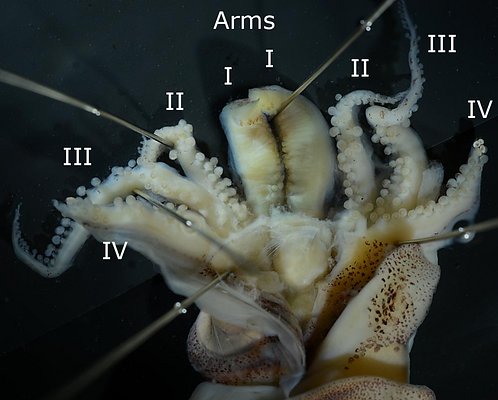
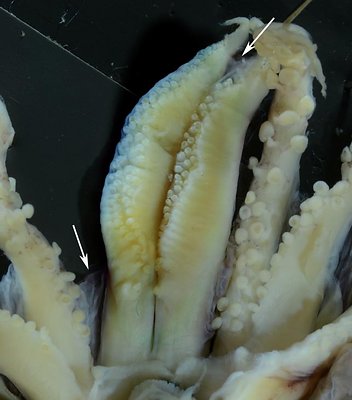
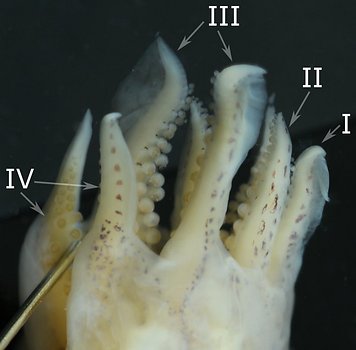
Figure. Oral views of the arms of Stoloteuthis sp. A, males. Left - The entire brachial crown, 16 mm ML,note the modified arms I and the stubby arms IV with modified suckers at their tips; tentacles lost during capture. Right - A larger specimen, 20 mm ML, but in poor condition, showing the modified arms I and the very long but narrow web that joins them (top arrow) and the very short web that connects to arms II (bottom arrow).
- Hectocotylus - Both arms I very thick, and with complex structure. Protective membranes larger on dorsal margins; secondary membranes passing from protective membrane, between suckers to midline of arm. Long, slender structures beneath surface on both lateral and medial sides of arms (apparently elongate sucker pedicles). Suckers in 2 series at arm base but in 3 or more irregular series in mid-arm (most apparent in largest male).
- Arm webs - Arms I with narrow, web between them that extends to the arm tips nearly binding them together.
- Suckers - Suckers of arms IV smaller than on other arms in mid-arm regions, but suckers at arm tips not greatly diminished in size; 4 terminal arm-tip suckers with opaque white tissue surrounding inner sucker rings. Arm II-IV without enlarged suckers. Most suckers globular with cup-shaped outer rings. Hectocotylus suckers globular at base but, distally, become more tubular and curved.
 Click on an image to view larger version & data in a new window
Click on an image to view larger version & data in a new window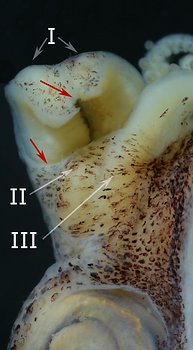
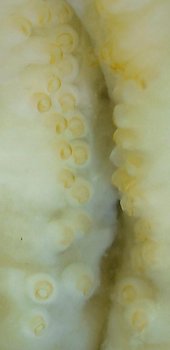
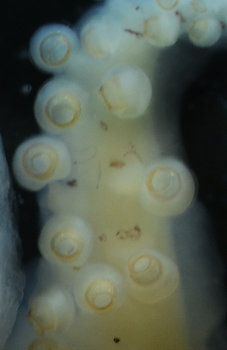
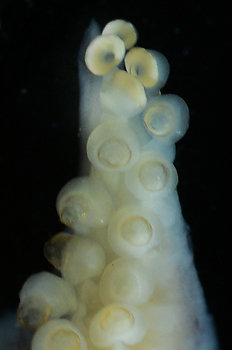
Figure. Stoloteuthis sp. A, male, 16 mm ML. Left - Side view of web between arms I near arm tip (top red arrow) and much lower between arms I and II (lower red arrow). Left middle - Oral view of basal 2/3 of arms I showing curvature of some suckers. Right middle - Arm II segment at 2/3 of arm from base showing typical globular suckers. Right - Tip of arm IV showing 4 white, distal suckers.
- Arm formula: III>I=II>IV. Arms I and IV rather blunt; arms II and III attenuate; arms I very broad broad (hectocotylized); all arms without broad distal keels.
- Head
- Small ocular pore on secondary eyelid just anterior to lens (usually difficult to locate).
 Click on an image to view larger version & data in a new window
Click on an image to view larger version & data in a new window
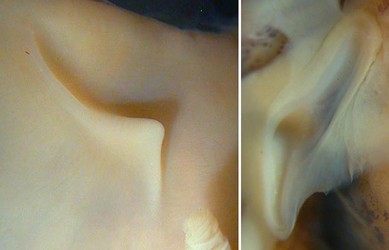
Figure. Dorsolateral view of the head of Stoloteuthis sp. A, female, 12 mm ML, showing the ocular pore (arrow). Photograph by R. Young.
- Small ocular pore on secondary eyelid just anterior to lens (usually difficult to locate).
- Funnel
- Funnel component of the funnel/mantle locking-apparatus slightly boomerang-shaped with deep, angular pit at bend and narrow grooves on either limb. Mantle component with slender ridges extending to a high point at bend which is in posterior half of lock. Anterior edge does not reach mantle margin.
- Funnel connected to head by broad funnel adductor muscles that attach to funnel near distal sides of funnel lock.
- Funnel component of the funnel/mantle locking-apparatus slightly boomerang-shaped with deep, angular pit at bend and narrow grooves on either limb. Mantle component with slender ridges extending to a high point at bend which is in posterior half of lock. Anterior edge does not reach mantle margin.
- Mantle
- Mantle margin free but nuchal cartilage fused to mantle.
- Ventral mantle shield confined to anterior half of mantle (see photograph under "Photophores").
- Mantle margin free but nuchal cartilage fused to mantle.
- Pigmentation/iridophores
- Thick iridophore layer present on posteroventral surface of funnel.
 Click on an image to view larger version & data in a new window
Click on an image to view larger version & data in a new window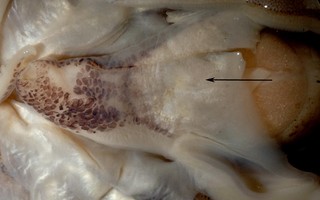
Figure. Ventral view of the funnel of Stoloteuthis sp. A female, 12 mm ML, showing iridophore layer (arrow). Photograph by R. Young.
- Thick iridophore layer present on posteroventral surface of funnel.
Comments
More details of the description of Stoloteuthis sp. A can be found here.
A better understanding of the structure of the male hectocotylus along with that of other species of Stoloteuthis and of Sepiolina nipponensis is needed before the relationships of Stoloteuthis sp. can be properly determined.
Discussion of Phylogenetic Relationships
The following table shows how some of the more phylogenetically important features in ggenera compare with those characters in Stoloteuthis sp. A. This is a simplified look at the genera and is simply to indicate that placing Stoloteuthis sp. A in a known genus is not easy. We have placed most emphasis on hectocotyliation which, as defined here shows similarities between Stoloteuthis sp. A and other Stoloteuthis spp. and Sepiolina in the special modification of arm I (although the type of modification may prove to only superficially similar). The structure of the club in the latter prevents placing Stoloteuthis there. We are basically using Stoloteuthis as a catch-all genus as it is already difficult to define with the inclusion of S. weberi.
| Hectocotylization | |||||||||
| club expanded | Tentacular organ | Shield length as % of VML | Photophore pores | Mantle-head fusion | Funnel locking- apparatus | Hectocotylization symmetrical | Web sector I - long; sector II - short | 1° hecto* = arms I | |
| Heteroteuthis | no | yes | ~50 | central | no | groove | no | no | no |
| Iridoteuthis | no | yes | >80 | side | yes | groove or groove & pit | yes | no | no |
| Nectoteuthis | no | yes | >80 | ? | no | groove & 2 pits | yes ? | no | no |
| Amphorateuthis | no | yes | >80 | side | yes | groove & pit | yes | no | no |
| Stoloteuthis | no | yes | >80 | central | yes or no | groove | yes | no | yes |
| Stoloteuthis sp.A | no | yes | ~50 | central | no | Groove & pit | yes | yes | yes |
| Sepiolina | yes | no, insipient | >80 | central | yes | groove | yes | yes | yes |
Title Illustrations

| Scientific Name | Stoloteuthis sp. A |
|---|---|
| Location | Waters off New Caledonia |
| Comments | Initially frozen, then thawed and photographed. |
| Specimen Condition | Dead Specimen |
| Sex | Female |
| Life Cycle Stage | Mature |
| View | Dorsolateral |
| Size | 13 mm ML |
| Copyright | © Jeff Dubosc |
About This Page

University of Hawaii, Honolulu, HI, USA
Correspondence regarding this page should be directed to Richard E. Young at
Page copyright © 2014
 Page: Tree of Life
Stoloteuthis sp. A.
Authored by
Richard E. Young.
The TEXT of this page is licensed under the
Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial License - Version 3.0. Note that images and other media
featured on this page are each governed by their own license, and they may or may not be available
for reuse. Click on an image or a media link to access the media data window, which provides the
relevant licensing information. For the general terms and conditions of ToL material reuse and
redistribution, please see the Tree of Life Copyright
Policies.
Page: Tree of Life
Stoloteuthis sp. A.
Authored by
Richard E. Young.
The TEXT of this page is licensed under the
Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial License - Version 3.0. Note that images and other media
featured on this page are each governed by their own license, and they may or may not be available
for reuse. Click on an image or a media link to access the media data window, which provides the
relevant licensing information. For the general terms and conditions of ToL material reuse and
redistribution, please see the Tree of Life Copyright
Policies.
- First online 03 November 2013
- Content changed 21 January 2014
Citing this page:
Young, Richard E. 2014. Stoloteuthis sp. A. Version 21 January 2014 (under construction). http://tolweb.org/Stoloteuthis_sp._A/149536/2014.01.21 in The Tree of Life Web Project, http://tolweb.org/










 Go to quick links
Go to quick search
Go to navigation for this section of the ToL site
Go to detailed links for the ToL site
Go to quick links
Go to quick search
Go to navigation for this section of the ToL site
Go to detailed links for the ToL site